The planet we call home is sending us urgent signals. From unprecedented heatwaves scorching cities to devastating floods reshaping coastlines, climate change has moved from a distant future threat to a present-day reality affecting every corner of our world. The evidence is overwhelming: 2024 marked the warmest year on record, with global temperatures exceeding 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels for the first time, atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations reaching heights not seen in 800,000 years, and extreme weather events displacing millions of people worldwide.
My name is Al, and I’m here to guide you through understanding one of the most critical challenges of our time. Whether you’re concerned about your family’s future, curious about the science, or ready to take action in your own life, this article will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to become part of the solution. Together, we’ll explore what’s causing these dramatic changes, how they’re affecting our daily lives, and—most importantly—the practical steps each of us can take to make a difference. Let’s dive into understanding climate change and discover how your choices can help shape a healthier, more sustainable future for generations to come.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect: The Science Behind Warming
The Natural Balance: Earth’s atmosphere acts like a protective blanket, trapping just enough heat to keep our planet at a comfortable average temperature of about 15°C (59°F). This natural greenhouse effect has sustained life for millions of years, with gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide capturing infrared radiation reflected from Earth’s surface and preventing it from escaping into space.
Human Disruption: Since the Industrial Revolution, human activities have dramatically altered this delicate balance. By burning fossil fuels for energy, clearing forests, and intensive agriculture, we’ve increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by more than 50% and methane by over 150%. In 2024 alone, global greenhouse gas emissions reached their highest levels ever recorded, with carbon dioxide levels soaring to 422.8 parts per million—a new record high.
Amplified Warming: Different greenhouse gases trap heat with varying effectiveness. Methane, for instance, is 86 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period, making it a particularly concerning contributor despite its lower atmospheric concentration. These gases don’t just trap heat directly—they trigger feedback loops that amplify warming. As temperatures rise, Arctic ice melts, exposing darker ocean water that absorbs more sunlight, which accelerates further melting in a self-reinforcing cycle.

Understanding these mechanisms is crucial because it shows us that every ton of emissions we prevent today helps break these dangerous feedback loops and limits future warming. With this foundation in how climate change works at the molecular level, let’s examine the specific human activities driving this global transformation.
The Main Culprits: What’s Driving Climate Change
Fossil Fuel Combustion: The single largest driver of climate change is burning coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity, transportation, and heating. In 2024, fossil fuel emissions hit a record high of 38.2 billion tons of CO₂, despite growing renewable energy capacity. Power plants, factories, vehicles, and buildings collectively account for the vast majority of these emissions, with the transportation sector alone responsible for about one-fifth of global emissions.
Deforestation and Land Use: The world’s forests, particularly the Amazon rainforest, serve as critical carbon sinks that absorb roughly 2.6 billion tons of CO₂ annually. However, deforestation for agriculture and development is destroying these natural climate regulators at alarming rates. In 2024, the Amazon experienced its worst forest fire season in over two decades, releasing an estimated 791 million tons of carbon dioxide—roughly equivalent to Germany’s annual emissions. This represents a devastating tipping point: for the first time, fire-induced forest degradation has overtaken deforestation as the primary driver of Amazon carbon emissions.
Agricultural Practices: Modern agriculture contributes significantly through multiple pathways. Livestock farming generates massive methane emissions from cattle digestion, while rice paddies and manure management add further greenhouse gases. Synthetic fertilizers release nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas 265 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Additionally, clearing land for grazing and crops eliminates carbon-absorbing vegetation while releasing stored carbon from soils.
Industrial Processes: Manufacturing, chemical production, and cement production release substantial emissions both from energy use and chemical reactions inherent to these processes.

The interconnected nature of these sources means addressing climate change requires transformation across all sectors of our economy and daily lives. Now let’s look at the hard data that makes the reality of these changes undeniable.
Visualizing the Impact: Graphical Evidence of Climate Change
The scientific consensus on climate change is strongly supported by multiple lines of empirical evidence. The following five key indicators collectively provide a comprehensive visualization of climate change’s progression and impacts over time. Each graph represents a critical measurement that scientists use to track Earth’s changing climate system, from atmospheric composition to physical manifestations in our oceans and ice sheets.
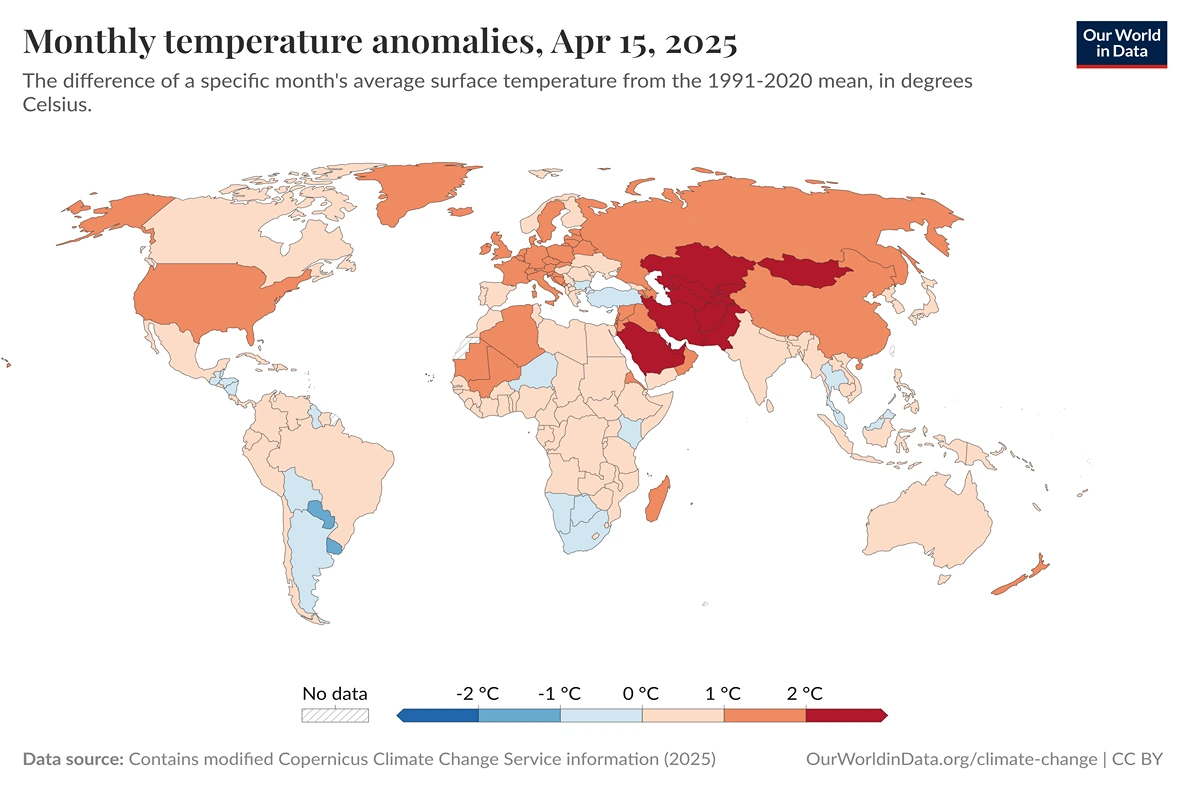
Global Temperature Rise Accelerating: This graph illustrates monthly temperature anomalies from 1940 to the present, revealing a clear warming trend that has accelerated in recent decades. The visualization shows deviations from the long-term average temperatures, with particularly pronounced warming occurring since the 1980s. The last decade stands out as the warmest on record, with global temperature anomalies frequently exceeding 1°C above pre-industrial levels. This warming pattern closely correlates with increased greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
Credit: Copernicus Climate Change Service (2019) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Monthly temperature anomalies” [dataset]. Copernicus Climate Change Service, “ERA5 monthly averaged data on single levels from 1940 to present 2” [original data]. Retrieved April 3, 2025 from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/monthly-temperature-anomalies
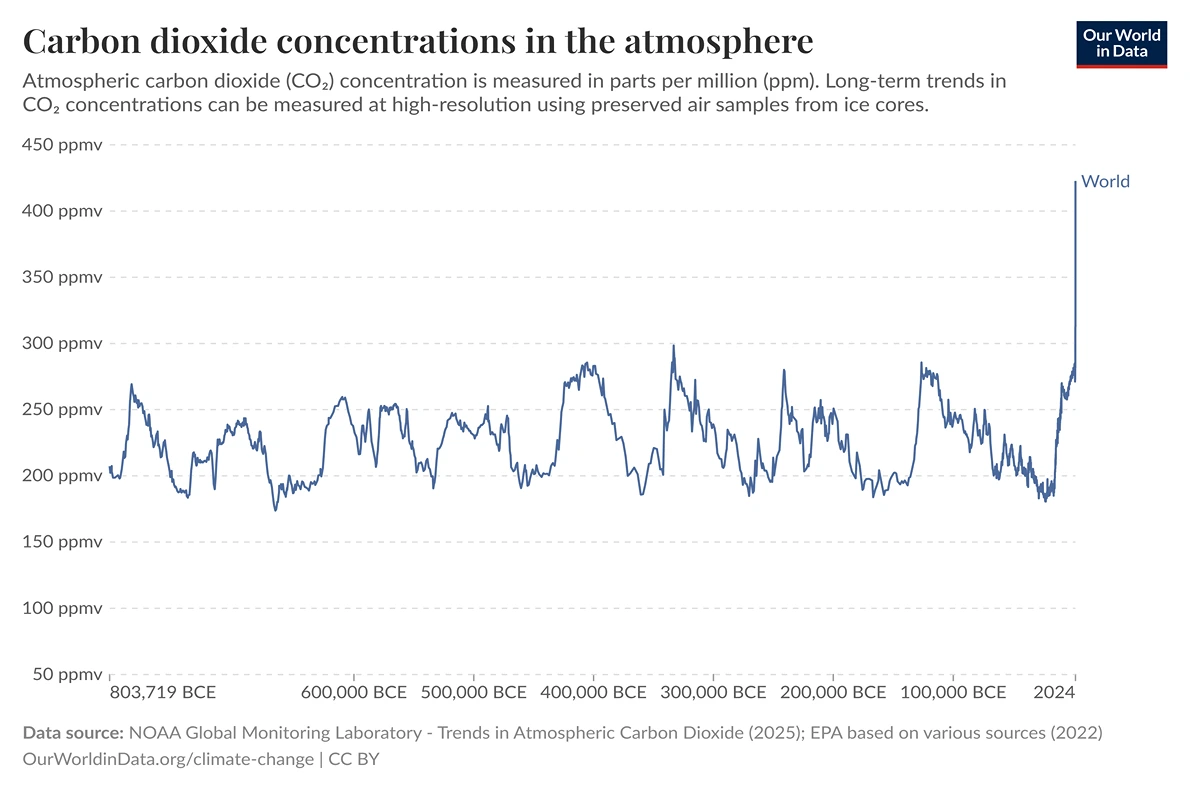
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide at Unprecedented Levels: This graph displays atmospheric CO₂ concentrations from 800,000 BCE to the present, providing crucial historical context for current climate change. For hundreds of thousands of years before the Industrial Revolution, CO₂ levels naturally fluctuated between approximately 180-280 parts per million (ppm). However, since the mid-19th century, concentrations have risen dramatically, surpassing 420 ppm in recent years—levels not seen in at least 800,000 years. This unprecedented rate of increase directly corresponds with human fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, establishing a clear causal link between human activities and changing atmospheric composition.
NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory – Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide (2024); EPA based on various sources (2022) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere” [dataset]. NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory, “Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide”; United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Climate Change Indicators: Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases” [original data]. Retrieved April 3, 2025 from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/co2-long-term-concentration
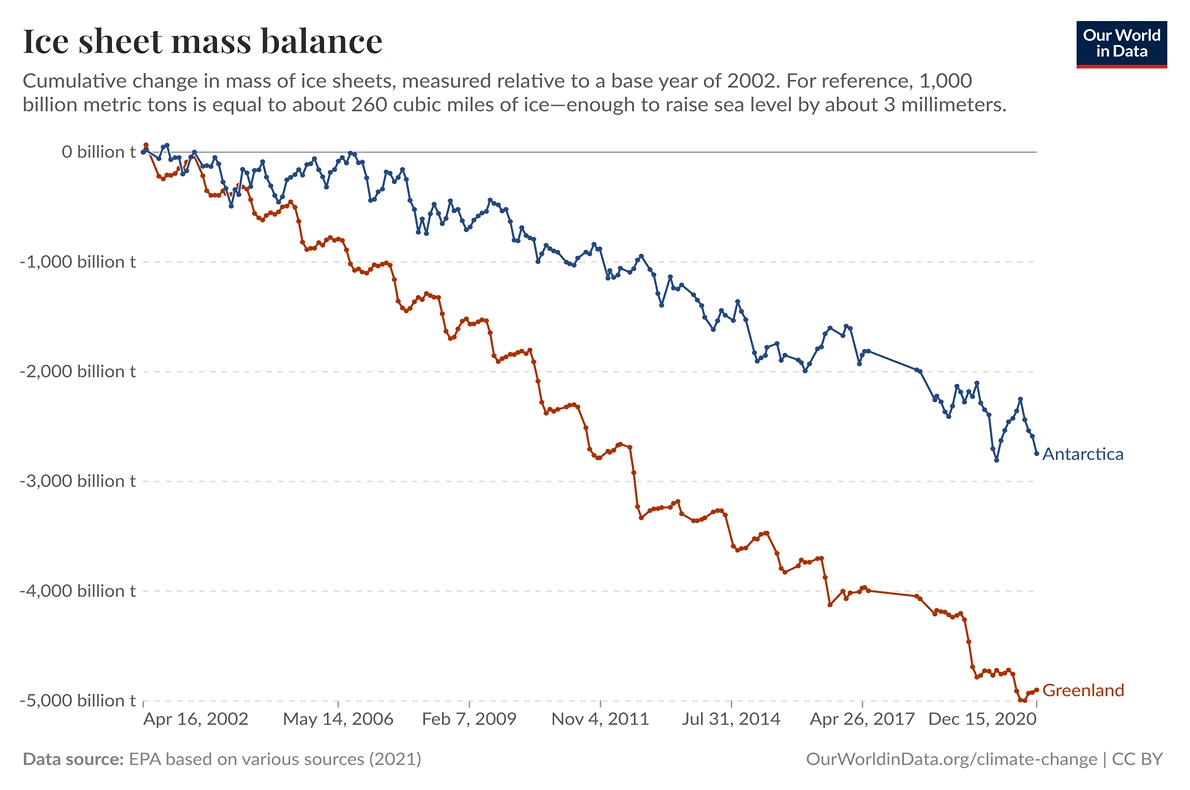
Dramatic Ice Sheet Melt at Both Poles: This graph illustrates the ice sheet mass balance of Greenland and Antarctica from 2002 to the present, quantifying the significant ice loss occurring at both poles. Satellite measurements show that Greenland has lost approximately 4,000 billion tons of ice since 2002, while Antarctica has lost around 2,500 billion tons during the same period. These losses have accelerated over time, with recent years showing more rapid decline than earlier measurements. The warming atmosphere and oceans, driven by increased greenhouse gas concentrations, are the primary drivers of this accelerating ice loss, which has direct implications for global sea level rise.
EPA based on various sources (2021) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Ice sheet mass balance – NASA/JPL” [dataset]. United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Climate Change Indicators: Ice Sheets” [original data]. Retrieved April 3, 2025 from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/ice-sheet-mass-balance
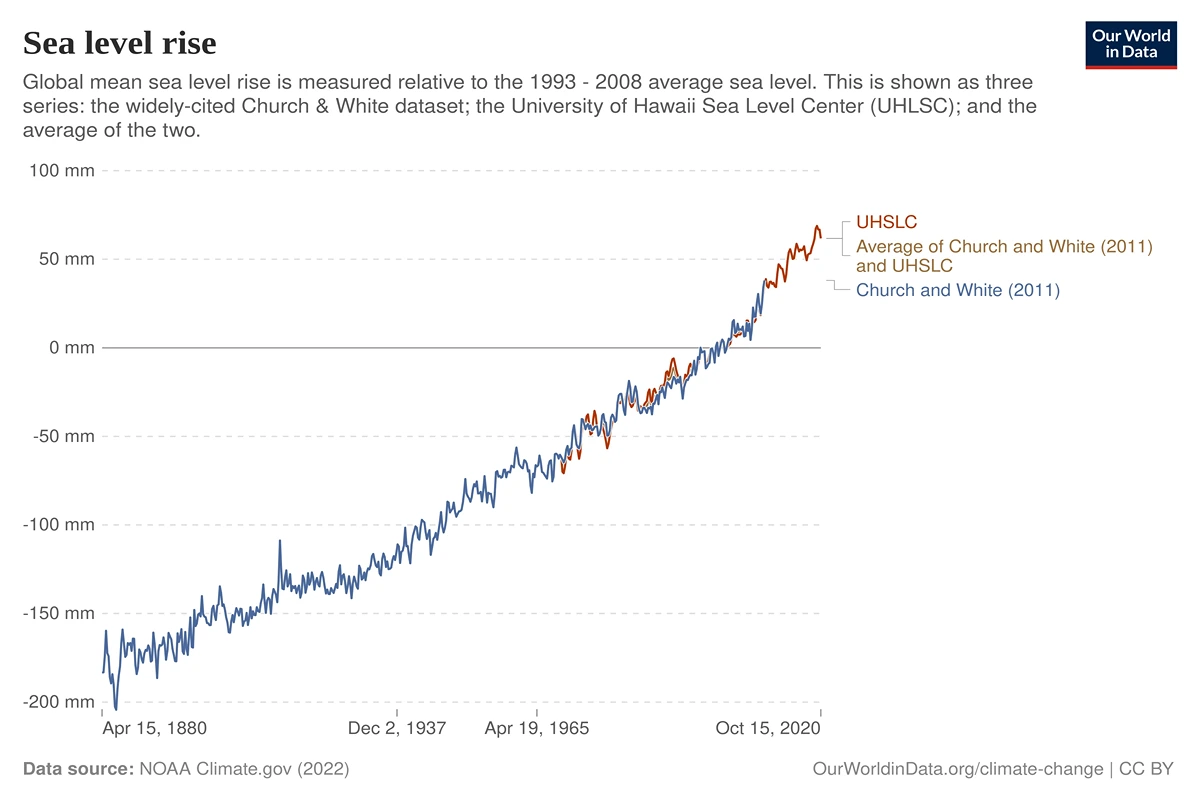
Global Sea Levels Rising Steadily: This graph tracks global sea level variations from 1880 to the present, demonstrating a clear upward trend that has accelerated in recent decades. Since 1880, global sea levels have risen by approximately 21-24 centimeters (8-9 inches), with about one-third of this increase occurring since 1993. This rising trend is primarily attributed to two climate change-driven processes: thermal expansion of seawater as ocean temperatures rise and increased water volume from melting land ice (including the ice sheets tracked in the previous graph). The acceleration in the rate of sea level rise closely follows the patterns of global warming and ice mass loss.
NOAA Climate.gov (2022) – processed by Our World in Data. “Global sea level according to Church and White (2011)” [dataset]. NOAA Climate.gov, “Climate Change: Global Sea Level” [original data].
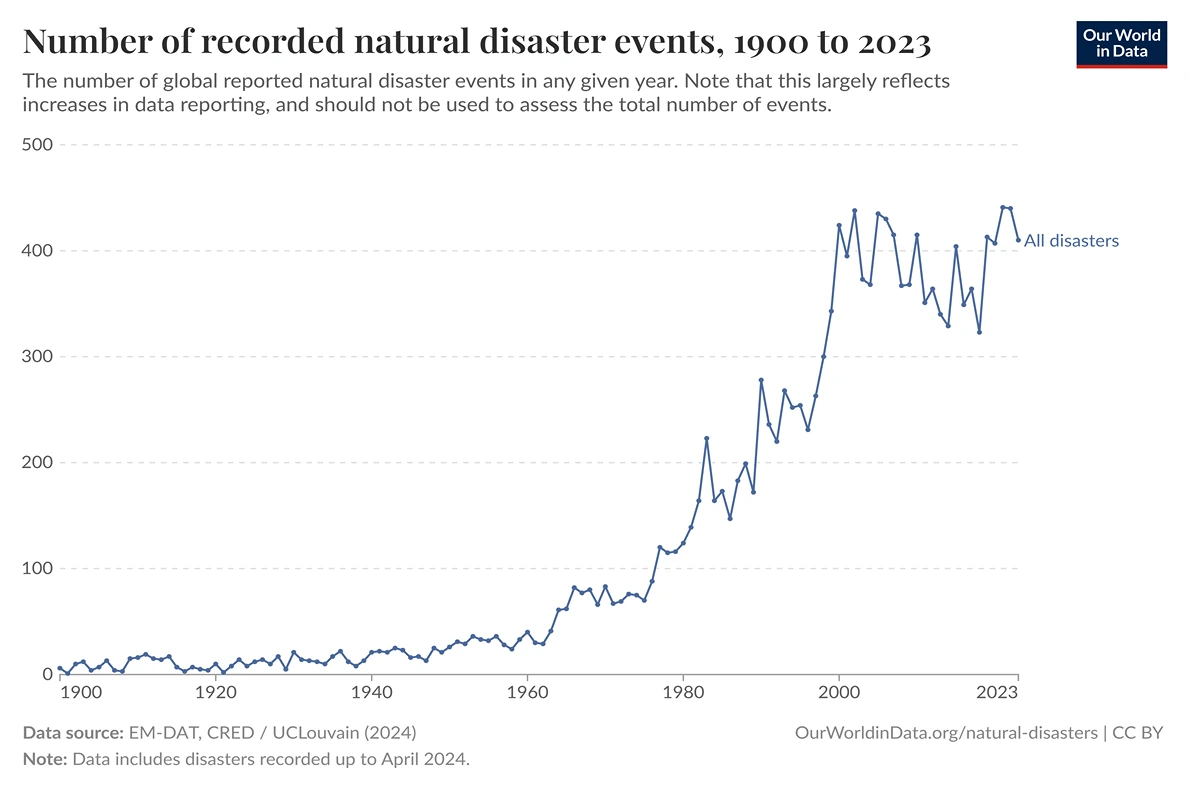
Natural Disaster Events Increasing Globally: This graph displays the frequency of recorded natural disaster events globally from 1900 to the present, showing a significant increase over time. While improved reporting and data collection account for some of this trend, climate change is increasingly recognized as a contributing factor that intensifies certain disaster types. Climate scientists have established with high confidence that warming temperatures increase the frequency and severity of heat waves, intensify precipitation patterns (leading to both flooding and drought), and can exacerbate wildfire conditions. The graph illustrates the growing human and economic costs associated with these climate-related hazards.
EM-DAT, CRED / UCLouvain (2024) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Number of recorded natural disaster events – EM-DAT” [dataset]. EM-DAT, CRED / UCLouvain, “Natural disasters” [original data]. Retrieved April 3, 2025 from https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/number-of-natural-disaster-events
The evidence presented through these five visualizations creates a coherent and comprehensive picture of climate change’s physical manifestations. These indicators are interconnected: increasing carbon dioxide concentrations drive rising global temperatures, which in turn accelerate ice sheet melt and sea level rise. These changing environmental conditions contribute to more frequent and intense extreme weather events and natural disasters.
The data reveals not only the current state of our climate system but also the alarming rate of change. Most striking is the temporal correlation between industrial development, fossil fuel consumption, and the acceleration of these climate indicators—particularly since the mid-20th century. The graphs illustrate that current changes are occurring at rates unprecedented in recent geological history.
With this robust visual evidence establishing the reality and urgency of climate change, we can now examine how these changes are already affecting lives and ecosystems around the world.
How Climate Change Touches Every Life
Extreme Weather Intensification: Climate change is fundamentally altering weather patterns worldwide. Hurricanes draw energy from warm ocean water, and as seas heat up, storms become more powerful and intensify faster. In September 2024, Hurricane Helene caused historic flooding across the southeastern United States, with over 200 deaths—fueled by exceptionally warm ocean waters. Meanwhile, droughts have intensified across multiple continents, with the American West experiencing a megadrought ranking among the worst in 1,200 years.
Ocean Changes and Marine Life: The oceans have absorbed about 90% of excess heat from global warming and roughly 30% of human-caused carbon dioxide emissions. This dual impact is devastating marine ecosystems. Ocean acidification—sometimes called “osteoporosis of the sea”—weakens the calcium carbonate structures that corals and shellfish need to build their skeletons. Combined with warming waters that cause coral bleaching, scientists project that 70-90% of coral reefs could disappear at 1.5°C warming, with up to 99% lost at 2°C.
Food Security Under Threat: Agriculture faces mounting challenges as climate change disrupts growing seasons and reduces yields. Heat stress decreases crop productivity, changing rainfall patterns create unpredictable growing conditions, and pest outbreaks intensify. In southern Africa, severe 2024 drought reduced maize production by more than 50%, leaving 30 million people facing food shortages. Even crops that survive higher temperatures may have reduced nutritional value, compounding food security concerns.
Health Impacts: Rising temperatures directly threaten human health through heat-related illnesses, with climate change adding an estimated 41 days of dangerous heat in 2024. A new study projects that years of healthy life lost to cardiovascular disease caused by hot weather could more than double by 2050 if current trends continue. Beyond heat, climate change expands the geographic range of disease-carrying insects and worsens air quality.
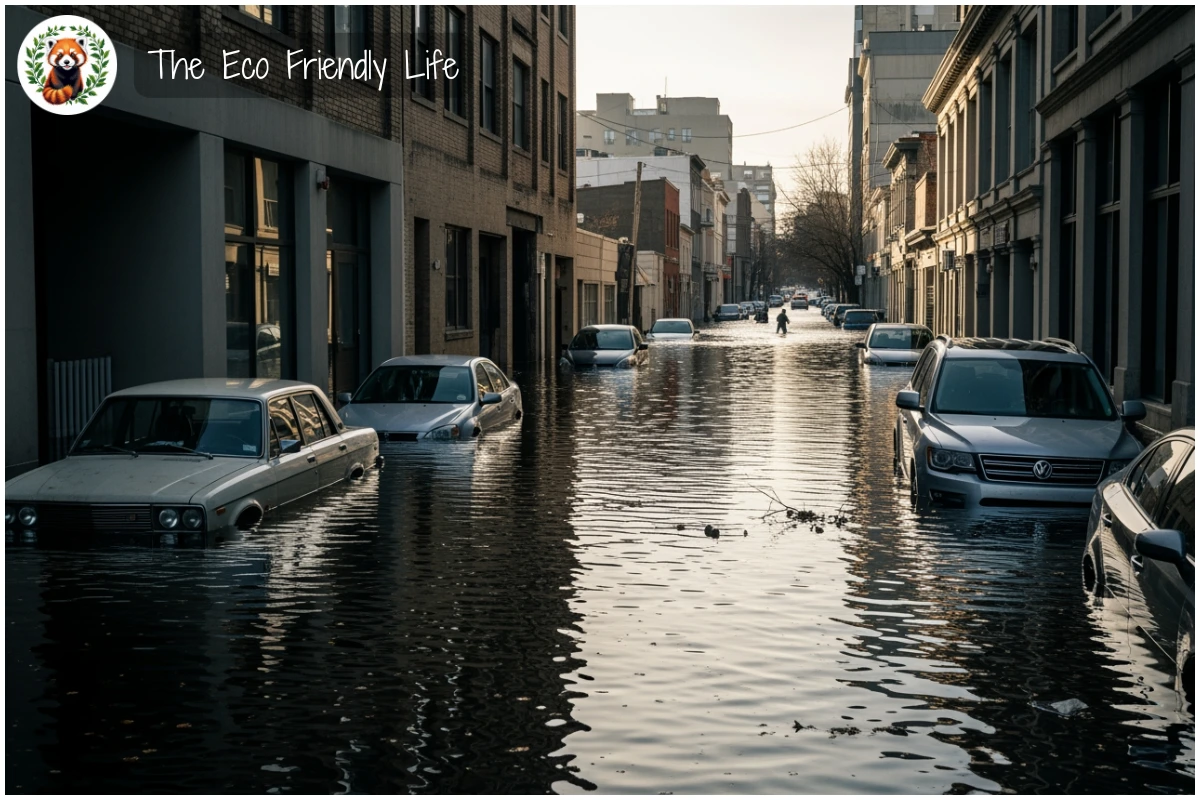

These interconnected impacts demonstrate that climate change isn’t a distant future problem—it’s reshaping lives and livelihoods right now, particularly affecting the world’s most vulnerable communities. Fortunately, powerful solutions exist, and understanding them begins with education—which is where our recommended resources can help.
Retailers That Support the Planet – Our Product Recommendations
Taking action on climate change starts with education and engagement, and the following retailers offer valuable resources to deepen your understanding and inspire sustainable living for you and your family.
Our Retailer Recommendation for Adults
edX – Learn Climate Solutions From Leading Universities
edX provides world-class online courses that empower individuals and professionals to understand and address climate change. The platform offers programs like Business and Climate Change: Towards Net Zero Emissions from the Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership, which teaches how to mitigate business risks and transition to net zero emissions over eight weeks of flexible online learning. Whether you’re a sustainability professional, business leader, or concerned citizen, edX’s climate change related courses offer practical knowledge from top universities to help you make informed decisions and lead change in your community.
Our Retailer Recommendation for Kids/Families
KiwiCo – Hands-On STEM Learning for Climate-Conscious Kids
KiwiCo delivers award-winning science and engineering projects that inspire environmental stewardship in children aged 2-16. Their subscription boxes include carefully designed projects focused on renewable energy, environmental science, and sustainable technology, with each kit taking over 1,000 hours to perfect. For families wanting to raise climate-aware children, KiwiCo’s STEM subscription kits transform complex environmental concepts into engaging hands-on activities, building critical thinking skills while fostering appreciation for our planet.
By investing in quality climate education for yourself and your family, you’re building the knowledge foundation needed to make meaningful environmental choices every day. Armed with this understanding, let’s explore the transformative solutions that are already changing our energy systems, transportation, and relationship with nature.
From Problem to Progress: Solutions Within Reach
Renewable Energy Revolution: The transition to clean energy is accelerating faster than many predicted. Solar and wind power have become the cheapest sources of electricity in most countries, with solar photovoltaics 41% cheaper and wind 53% cheaper than fossil fuel alternatives in 2024. Global renewable capacity grew by 15.1% in 2024, adding 585 gigawatts of new clean power—equivalent to powering hundreds of millions of homes. Battery storage costs have plummeted 93% over the past decade, solving the intermittency challenge and making 24/7 renewable power increasingly viable.
Sustainable Transportation: Electric vehicles are rapidly gaining market share, with EVs now comprising over 18% of new car sales globally. In Australia, over 91,000 battery EVs were sold in 2024, with costs falling and government incentives making the transition more accessible. EVs powered by renewable electricity produce 75% less carbon pollution than conventional vehicles while offering lower operating costs.
Nature-Based Solutions: Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems offers powerful climate benefits. Reforestation can sequester significant carbon while providing habitat for biodiversity, improving water quality, and supporting local communities. Coastal wetlands, when protected, can sequester an additional 290 million tons of CO₂ equivalent per year by 2050 while shielding communities from storms and floods.
Sustainable Agriculture: Shifting agricultural practices through agroforestry, regenerative farming, rotational grazing, and reduced tillage can simultaneously lower emissions and increase resilience. Plant-based diets offer particularly significant benefits—vegan diets produce up to 75% less greenhouse gas emissions and use 54% less water than omnivorous diets, while providing health benefits including lower risks of heart disease and diabetes.
Policy Frameworks: The Paris Agreement has kept climate action on the international agenda despite geopolitical challenges, with countries worldwide committing to net-zero emissions. Carbon pricing mechanisms—including carbon taxes and emissions trading systems—are creating economic incentives for businesses to reduce emissions while generating revenue for climate solutions.
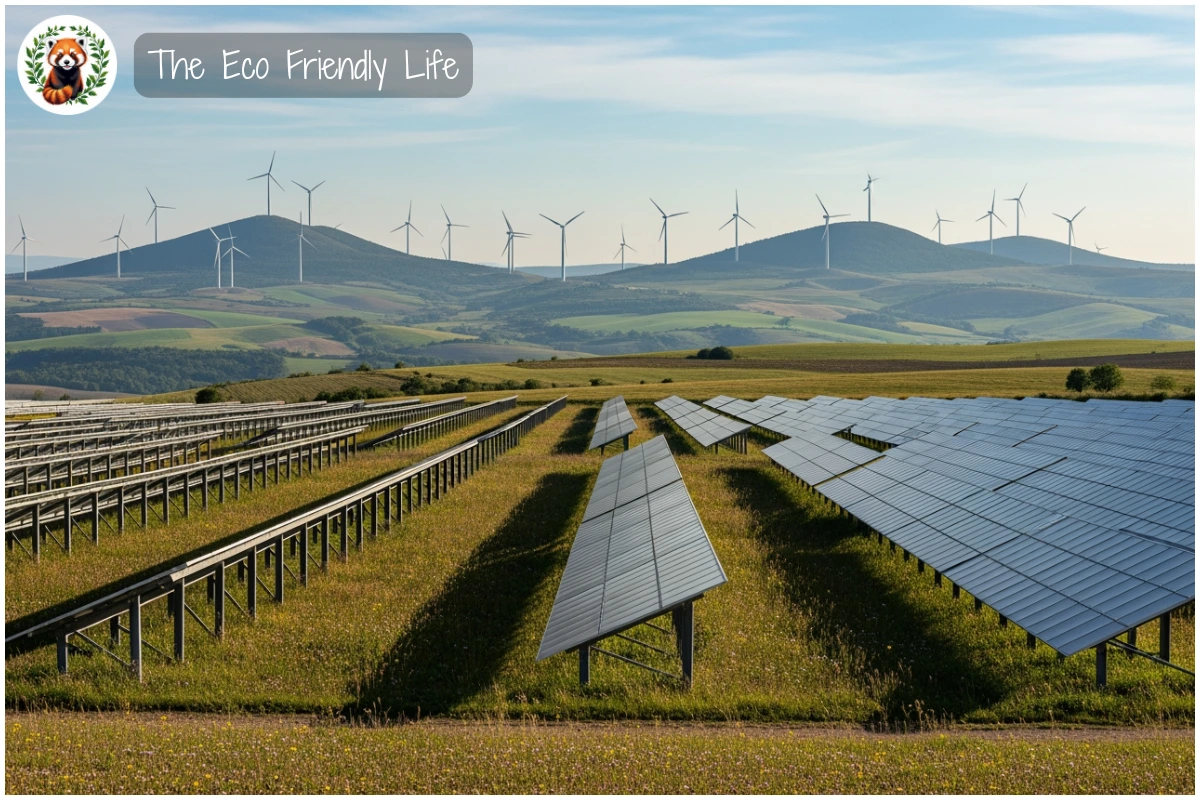

These solutions aren’t theoretical—they’re being implemented successfully around the world right now, proving that a sustainable future is achievable. Beyond these large-scale transformations, each of us has the power to make a difference through daily choices, so let’s explore the practical actions you can take starting today.
Practical Daily Tips You Can Action Today
| Action | How to Implement | Climate Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduce Energy Use | Switch to LED bulbs, unplug devices when not in use, adjust thermostat by 2-3 degrees. Install programmable thermostat. | Lowers your carbon footprint by reducing electricity demand from fossil fuel power plants. |
| Choose Plant-Based Meals | Start with “Meatless Mondays” or replace one meal daily with plant-based alternatives. Explore diverse cuisines. | Reduces agricultural emissions, as animal products generate 10-50 times more emissions than plant foods. |
| Switch Transportation | Walk, bike, or use public transit for short trips. Consider carpooling or electric vehicles for longer journeys. | Cuts transportation emissions, which account for roughly 20% of global carbon pollution. |
| Reduce Waste | Compost food scraps, choose reusable bags and containers, recycle properly, buy products with minimal packaging. | Prevents methane from landfills and reduces emissions from manufacturing new products. |
| Support Renewable Energy | Switch to a green energy provider or install solar panels if feasible. Advocate for community solar programs. | Directly reduces fossil fuel demand and supports clean energy infrastructure development. |
| Conserve Water | Fix leaks, take shorter showers, install water-efficient fixtures, collect rainwater for gardens. | Reduces energy used for water heating and treatment, lowering your overall carbon footprint. |
| Buy Sustainable Products | Choose items made from recycled materials, support companies with strong environmental policies, buy local when possible. | Reduces emissions from manufacturing and transportation while supporting sustainable business practices. |
| Reduce Food Waste | Plan meals, store food properly, use leftovers creatively, compost unavoidable scraps. | Prevents methane emissions from decomposing food in landfills and reduces agricultural resource waste. |
| Educate Yourself | Read climate science, follow environmental news from credible sources, take online courses about sustainability. | Empowers informed decision-making and helps you identify new opportunities for climate action. |
| Amplify Your Voice | Contact elected officials, support environmental organizations, discuss climate solutions with friends and family. | Collective advocacy drives policy changes that create systemic solutions beyond individual actions. |
Small changes add up—if everyone made just a few of these adjustments, the collective impact would be transformative. As you implement these personal actions, you might have questions about their effectiveness and the broader climate picture, so let’s address some common concerns.
FAQs
Can individual actions really make a difference when corporations are the biggest emitters? Absolutely. While systemic change is essential, individual actions create ripple effects by influencing markets, inspiring others, and building political will for policy changes. Moreover, our consumption choices directly drive corporate emissions.
Is it too late to prevent climate change? We’ve already experienced some warming, but every fraction of a degree matters. Limiting warming to 1.5-2°C versus 3°C or more dramatically reduces the severity of impacts, and many solutions are already available and economically viable.
What’s the single most impactful action an individual can take? Reducing meat consumption, particularly beef, choosing renewable energy, and using low-carbon transportation are among the highest-impact personal choices. However, advocating for systemic policy changes may ultimately have the greatest effect.
How can I cope with climate anxiety? Focus on actions within your control, limit news exposure, connect with climate action communities, and seek professional support if anxiety becomes overwhelming. Channeling concern into constructive action often provides relief.
Beyond individual action, supporting organizations working at scale can multiply your impact, so here are some of the most effective climate organizations you can support directly.
Organizations to Support – Our Recommendations
If you’re ready to support organizations working on the frontlines of climate action, consider these highly effective global nonprofits:
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) works across over 100 countries to preserve nature and wildlife while promoting a clean energy future and sustainable practices. Their science-based conservation projects protect endangered species, restore ecosystems, and advocate for climate-friendly policies. Support WWF’s climate work by contributing to their global conservation efforts that address both biodiversity loss and climate change simultaneously.
- Greenpeace uses direct action, lobbying, and scientific research to protect oceans, forests, and the climate across 55+ countries. Funded entirely by individual donors to maintain independence, Greenpeace has successfully prevented Arctic oil drilling and driven major corporate environmental commitments. Donate to Greenpeace to support their high-impact campaigns for climate justice.
- The Sierra Club mobilizes grassroots advocacy across 200+ local chapters, focusing on clean energy transition and conservation in North America. Their “Beyond Coal” campaign has contributed to retiring over 300 coal plants, driving significant emissions reductions. Support Sierra Club initiatives to fund direct policy change and community-level environmental justice work.
Your support helps these organizations continue their critical work protecting our planet for future generations. To deepen your understanding even further, explore these expert resources that provide comprehensive climate information.
Resources and Further Reading
For those seeking deeper understanding and authoritative information on climate change, these expert resources provide comprehensive, science-based insights:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Reports represent the gold standard of climate science, synthesizing research from thousands of scientists worldwide to provide authoritative assessments of climate change causes, impacts, and solutions. Access the latest IPCC for comprehensive scientific evidence and policy recommendations that inform global climate action.
- NASA Climate Change Resources offer accessible explanations of climate science, real-time data visualizations, and regularly updated information on Earth’s changing climate based on satellite observations and scientific research. Explore NASA’s climate portal for interactive tools, educational materials, and evidence-based information suitable for all knowledge levels.
- Our World in Data Climate Change Portal provides extensively researched articles with comprehensive data visualizations tracking global emissions, temperature changes, renewable energy growth, and climate impacts over time. Visit Our World in Data for evidence-based analysis that makes complex climate data accessible and understandable for everyone.
These resources empower you with the knowledge needed to understand climate change deeply and communicate effectively about solutions.
Our Related Articles

How We Can Help The Environment
The planet we call home faces unprecedented environmental challenges, from climate change and biodiversity loss to pollution and resource depletion. While these issues can feel…
Read More
Your Guide To Key Environmental Terms
Understanding the language of environmental science is the first step toward becoming an informed planetary citizen. Whether you’re hearing about climate policies on the news,…
Read MoreConclusion
Climate change represents the defining challenge of our generation, but it’s also an opportunity to build a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous world. The science is unequivocal: human activities are warming our planet at an unprecedented rate, with consequences already affecting millions of lives through extreme weather, ecosystem collapse, and threats to food and water security. Yet the solutions are equally clear—renewable energy is now cheaper than fossil fuels, sustainable agriculture can feed the world while restoring ecosystems, and individual choices collectively drive massive change.
Every action matters. Whether you’re switching to renewable energy, reducing meat consumption, advocating for policy change, or educating others, your choices ripple outward, influencing markets, inspiring communities, and building momentum for the systemic transformation we urgently need. The window to limit warming to 1.5°C is rapidly closing, but with determined action across all sectors of society, we can still create a livable future for generations to come.
Now it’s your turn to be part of the solution. What climate action will you commit to this week, and what challenges or questions do you have about making sustainable choices in your daily life? Share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments below—let’s learn from each other and build a community of climate action together.